06/10/2023, Miami Beach, FL. By Nima Schei, MD.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and cybersecurity are two of the most important and rapidly evolving technologies in the world today. They have the potential to transform various industries, especially fintech, which relies on data, automation and security to provide financial services to customers. However, AI and cybersecurity also pose significant challenges and risks, as malicious actors can exploit them for nefarious purposes. In this article, we will explore the multidimensional relationship between AI and cybersecurity and its impact on fintech, based on a panel conversation we had with experts in the field.
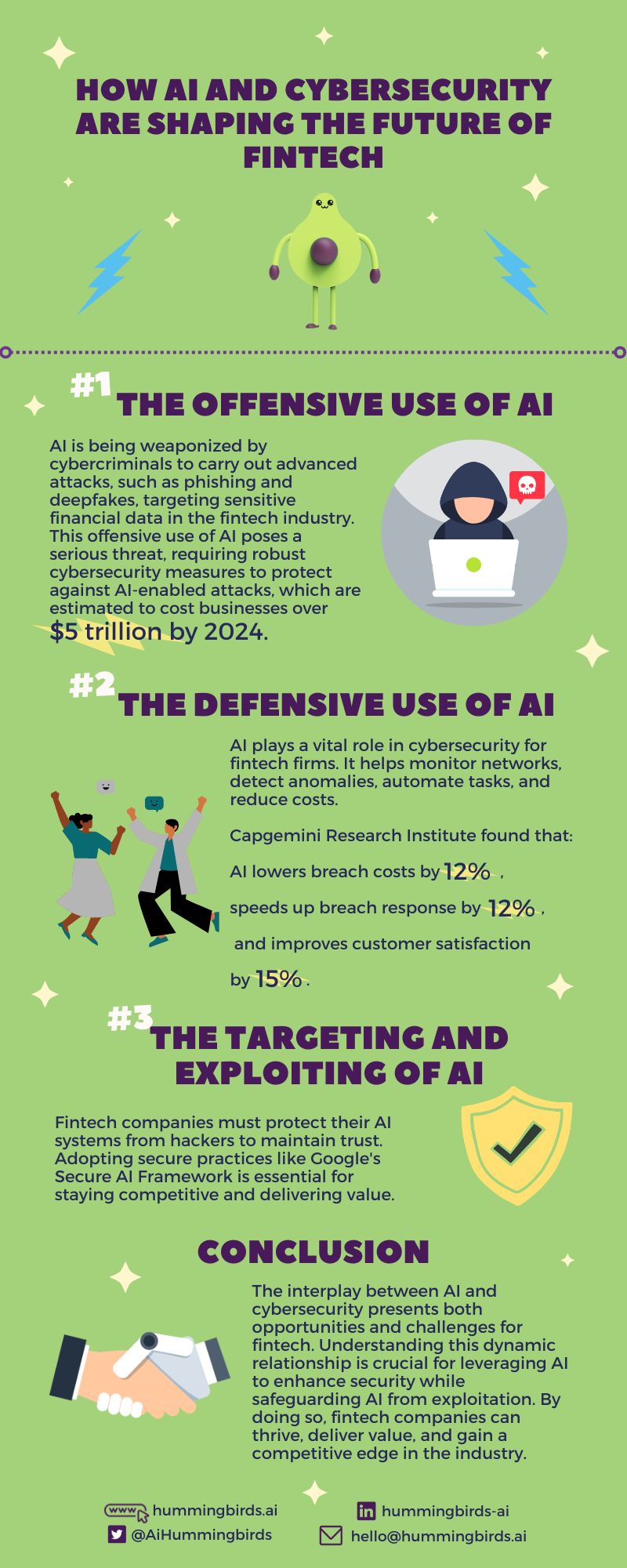
1. The Offensive Use of AI
One of the dimensions of the relationship between AI and cybersecurity is the offensive use of AI, where cybercriminals use AI to hack into systems, steal data, commit fraud and launch sophisticated attacks. For example, hackers can use AI to generate realistic phishing emails or voice calls that impersonate trusted entities, such as banks or government agencies, and trick users into revealing sensitive information or clicking on malicious links. Hackers can also use AI to create fake images or videos, known as deepfakes, that can be used to impersonate or blackmail individuals or organizations. That’s why I publicly stood against the mass release of deep fake technologies by mega tech companies (NTV interview). Moreover, hackers can use AI to analyze large amounts of data and find vulnerabilities or passwords in systems, or to create malware that can evade detection or adapt to different environments.
The offensive use of AI poses a serious threat to fintech companies, as they handle sensitive financial data and transactions that can be targeted by hackers for monetary gain or sabotage. According to a report by Juniper Research, cybercrime will cost businesses over $5 trillion by 2024, with financial services being one of the most affected sectors. Therefore, fintech companies need to invest in robust cybersecurity measures and solutions that can protect their data, systems and customers from AI-enabled attacks.
2. The Defensive Use of AI
Another dimension of the relationship between AI and cybersecurity is the defensive use of AI, where AI is used to fight against cyberattacks and enhance security. For example, AI can help fintech companies monitor their networks and systems for any anomalies or suspicious activities, and alert them in real time. AI can also help fintech companies analyze large amounts of data and identify patterns or trends that can help them improve their products, services or processes. Furthermore, AI can help fintech companies automate their security tasks and responses, such as scanning for vulnerabilities, patching systems, updating software or blocking malicious traffic.
The defensive use of AI can provide many benefits for fintech companies, such as reducing costs, increasing efficiency, improving customer experience and complying with regulations. According to a report by Capgemini Research Institute, 69% of organizations say that using AI in cybersecurity helps them reduce the cost of detecting and responding to breaches by an average of 12%. Additionally, 73% of organizations say that using AI in cybersecurity helps them respond faster to breaches by an average of 12%. Moreover, 64% of organizations say that using AI in cybersecurity helps them enhance customer satisfaction by an average of 15%.
3. The Targeting and Exploiting of AI
The third dimension of the relationship between AI and cybersecurity is the targeting and exploiting of AI itself, where cybercriminals try to manipulate or compromise the AI systems or models that are used by fintech companies. For example, hackers can try to poison the data that is used to train or test the AI models, such as adding noise or malicious inputs that can affect their performance or accuracy. Hackers can also try to extract confidential information from the AI models, such as the data they were trained on or the parameters they use. Hackers can also try to fool the AI models into making wrong decisions or predictions by generating adversarial examples that are designed to trick them.
The targeting and exploiting of AI can have serious consequences for fintech companies, as it can undermine their trustworthiness, reliability and reputation. According to a report by IBM Security and Ponemon Institute, 40% of organizations say they do not have measures in place to secure their AI platforms. Therefore, fintech companies need to adopt best practices and frameworks to secure their AI systems and models from potential attacks. For instance, Google recently launched its Secure AI Framework (SAIF), which is a conceptual framework that aims to help collaboratively secure AI technology based on six core principles:
- Expand strong security foundations to the AI ecosystem
- Extend detection and response to bring AI into an organization’s threat universe
- Automate defenses to keep pace with existing and new threats
- Harmonize platform-level controls to ensure consistent security across the organization
- Adapt controls to adjust mitigations and create faster feedback loops for AI deployment
- Contextualize AI system risks in surrounding business processes.
Conclusion
AI and cybersecurity are both powerful and disruptive technologies that can shape the future of fintech. However, they also have a complex and dynamic relationship that can pose opportunities and challenges for fintech companies. Fintech companies need to be aware of the different dimensions of this relationship and how they can leverage AI to enhance their security, as well as how they can protect their AI from being exploited. By doing so, fintech companies can gain a competitive edge and deliver value to their customers and stakeholders.